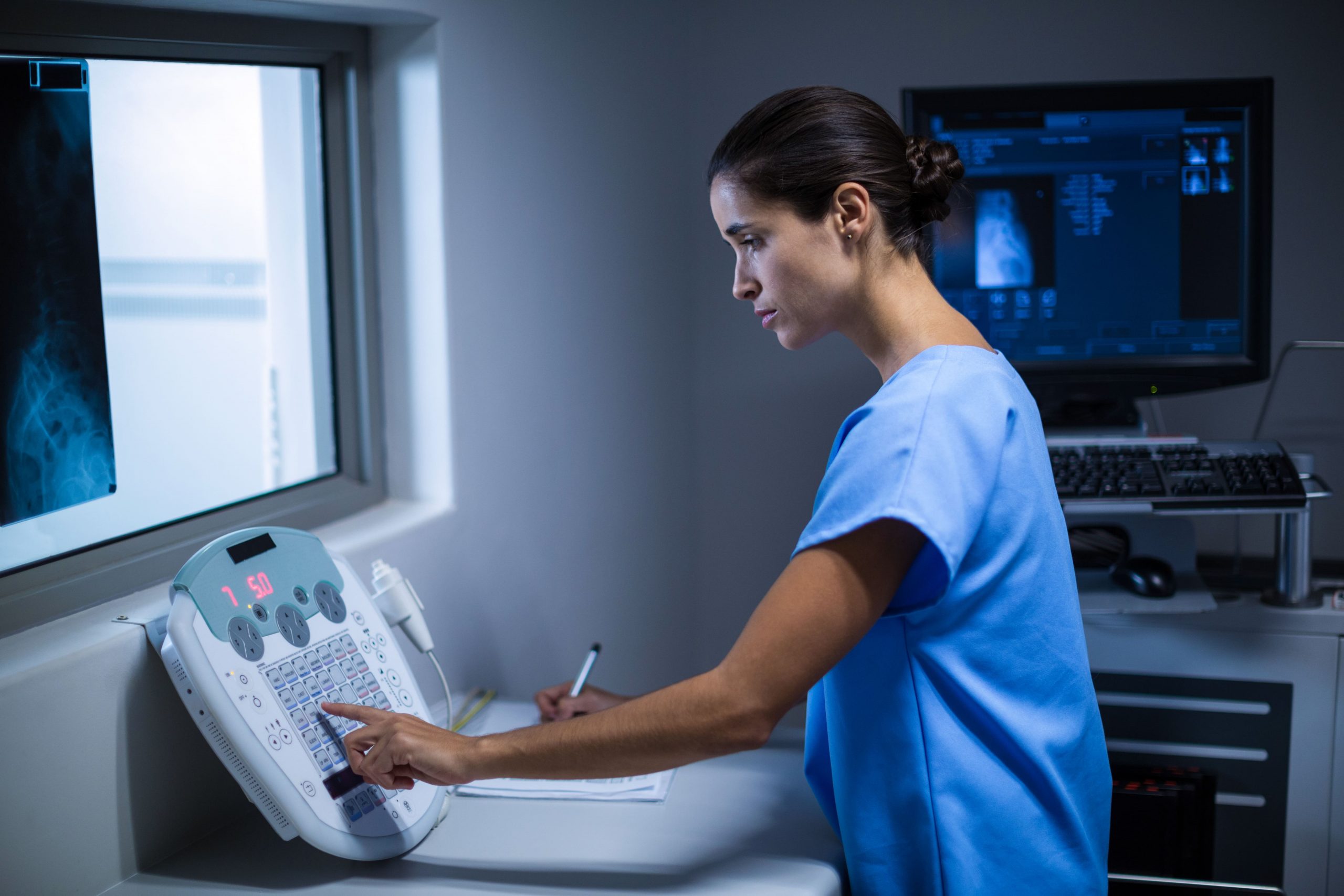
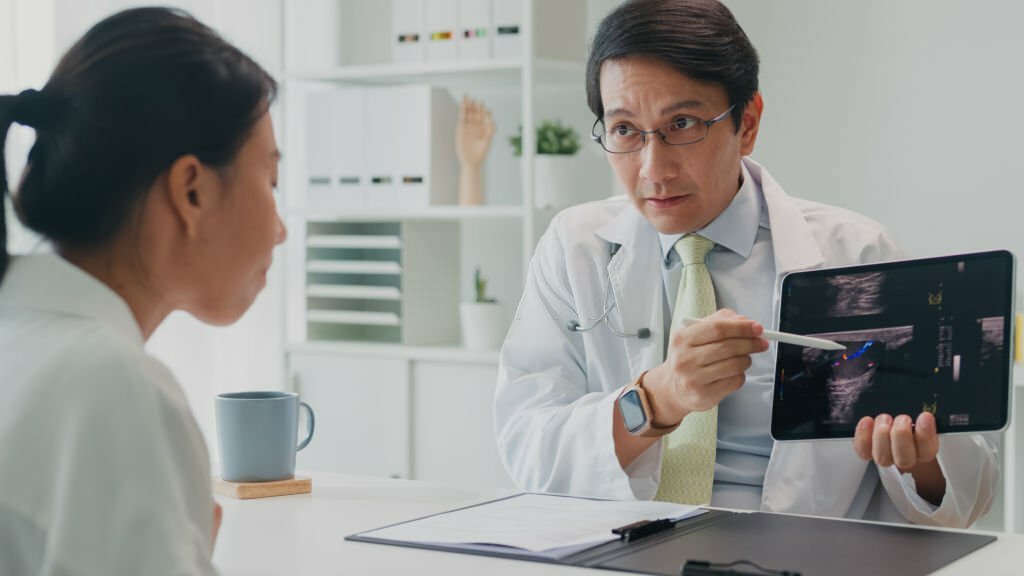
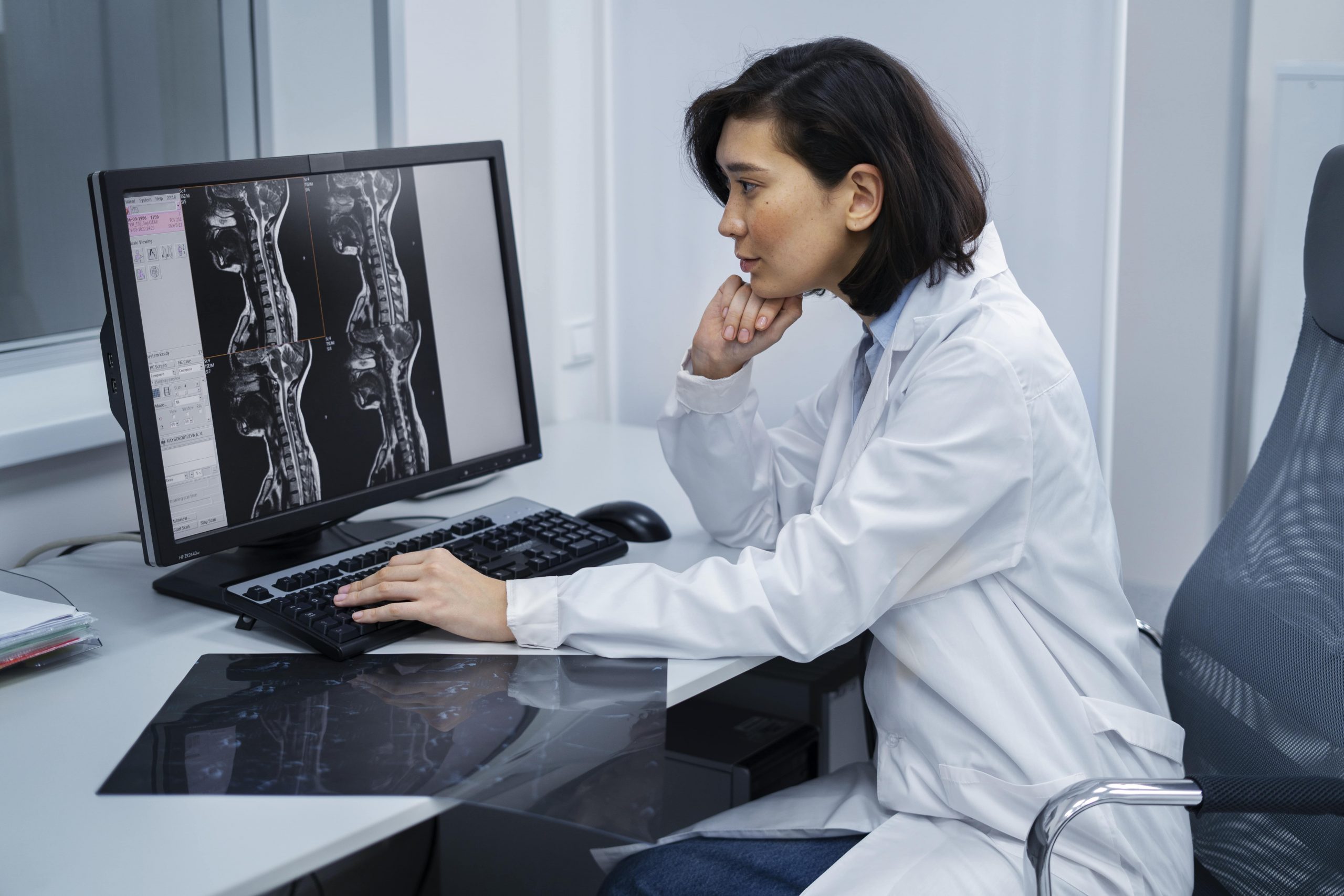
Have you ever gotten up with a pain of tightness in your chest and have no idea what happened? Maybe you forgot your water bottle at the gym, or didn’t even drink a sip. Whatever the reason, you can be certain that it could be dehydration.
Water is always good for your body. You are approximately 60% water; if you don’t drink the recommended amount, complications may arise. Because of dehydration, you feel pain in your chest. Reviewed by an expert at ViaScan, PhD. John Duncan, this guide will help you determine when dehydration is the cause of chest pain and when you should be concerned about your health. We will also explore how imaging tests can provide solutions. The following symptoms can be used to diagnose what is happening to you.
Are the chest pains related to dehydration, or do they indicate some other issue?
In most cases, the chest pain is caused by dehydration; however, most people believe that this is not a frequent occurrence. Having less water in your body means that your blood is thicker, and your heart needs to pump harder. Electrolyte levels can also be disturbed by dehydration, making minerals such as sodium and potassium imbalanced and causing the heart to beat abnormally. The loss in proportion can lead to chest pain or soreness.
Chest or lung conditions, such as a heart attack, angina, or a chest infection caused by a pulmonary or lung blood clot, may also be indicated by chest pain. You cannot assume dehydration is the cause and ignore other symptoms. Chest pain from dehydration is usually accompanied by other symptoms, such as very dark urine, dry mouth, and dizziness. When your chest pain is sudden or there are other severe symptoms, it is wise to get imaging tests for chest pain to determine serious disorders.
What dehydration symptoms are indicators of chest pain?
Feeling out of breath can easily give the deception of heart issues when you are dehydrated. The following signs should be observed:
- Rapid heart rate:
Low fluid levels can lead to a rapid heartbeat. It might feel like heart disease, but it is just your body responding to dehydration.
- Chest tightness or pressure:
With low body fluid in your chest, the muscles that surround the chest make that tight feeling, which can be very scary.
- Feeling lightheaded and dizzy:
Dehydration reduces blood pressure, making you feel dizzy. These are the symptoms that clinical pain associated with the chest may have, and lead to unreasonable worry.
- Shortness of breath
A sensation of Breathlessness is often due to a lack of sufficient fluid in the body. That causes difficulty in the passage of oxygen in and out, and your breathing becomes rapid or a challenge, and your chest tightens.
- Fatigue and weakness:
You feel quite tired, and weak, and heavy in the chest, and hard beset still to catch your breath.
What is the difference between a sore chest due to lack of hydration and a serious heart condition?
You can save your life by realizing the difference. An obvious contrast now follows so that you get to know what kind of pain you might be feeling these days:
| Dehydration-Related Chest Pain | Heart-Related Chest Pain |
| Usually feels like tightness or discomfort | Often feels like crushing pressure or squeezing |
| Improves after drinking water and resting | Doesn’t improve with hydration |
| Comes with dry mouth, dark urine, and thirst | May come with arm pain, jaw pain, or back pain |
| Happens after exercise, heat exposure, or not drinking water | It can happen at rest or with minimal activity |
| Heart rate is fast but regular | May have an irregular heartbeat or a very slow pulse |
| Gets better within 30 minutes to an hour | Persists or gets worse over time |
| Not accompanied by sweating or nausea (usually) | Often comes with cold sweats, nausea, or vomiting |
| Breathing improves with rest | Breathing difficulty continues or worsens |
This table provides a starting point; however, when in doubt, always seek a medical evaluation. Imaging tests for the chest, including heart and lung scans at facilities like ViaScan, can give definitive answers about what’s happening inside your body.
Should chest pain always be treated as a medical emergency?
Some forms of chest pain are the ones that you can’t afford to ignore. Call 911 right away when the chest pains are accompanied by one of these warning signs:
- The pains spread to your arm, jaw, neck, or back;
- The pains are squeezing and crushing in quality and are very intense.
- The pains come with cold sweat and/or a sense of nausea in your stomach, and you discover that you are having trouble breathing.
These signs can mean a heart attack or any other condition that leads to death.
Seek emergency care if chest trouble comes on suddenly and hurts, if you have
- high blood pressure,
- diabetes, smoking,
- and family history of heart disease.
Time is crucial with the heart. Even though you are a healthy young individual, any sudden acute chest pain without any other symptoms hints towards rapid diagnosis. There is pain in the chest that may be due to dehydration, and you cannot always keep a check on whether this is fine or not. Physicians have tools to check in less time whether your heart is under any danger or not, and provide you with life-saving therapy.
What immediate step should you follow if you feel that dehydration is causing your chest discomfort?
- Sit down and rest in some dark place. Cease any exercise.
- Take in water slowly, every 15 minutes. Don’t drink a lot at once, that will upset your stomach.
- As a medical professional, I suggest drinking an electrolyte or sports drink because it provides water and the minerals your body needs all at once.
Monitor your symptoms. Chest pain from dehydration must improve within 30 minutes once you drink fluids. Unless it improves, or gets more frequent, and you have new severe symptoms such as shortness of breath or pain in your arm, call emergency services immediately. Once the pain has disappeared, take a check-up routine appointment, particularly in case it is not the first time you have experienced the pain. The doctor will also perform a scan of your heart, chest, and lungs during your appointment, so that he can ensure everything is fine.
What types of tests does a doctor request to eliminate heart disease, or else dehydration?
When a person visits the doctor due to chest pain, the first examination will include simple tests.
- This usually begins with blood tests to assess electrolytes, kidney function, and enzymes in the heart, which increase whenever there is a heart injury.
- Next, an electrocardiogram (EKG) could reveal an issue in case of a possible heart attack or arrhythmia.
- Blood temperature and resistance to the oxygen supply in the blood provide immediate indications of your circulation.
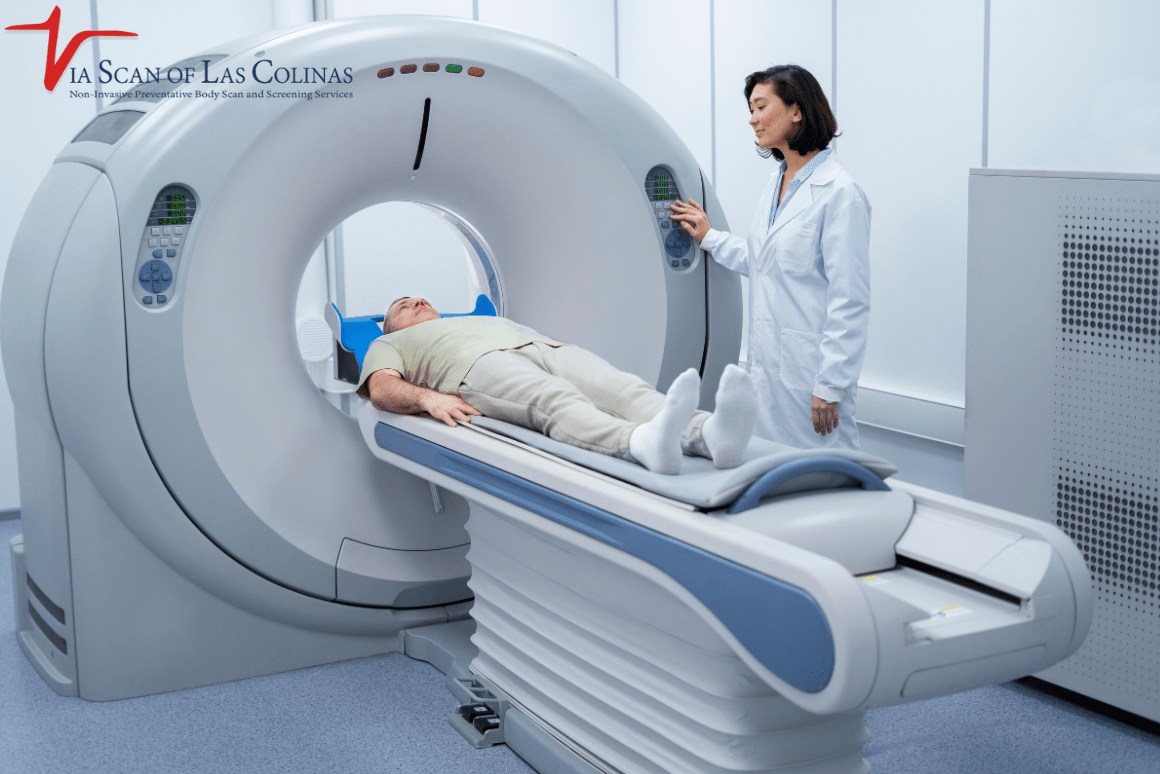
- To get a better look, or rather to have a closer examination of your body, there are imaging tests for chest pain that take detailed photographs.
In the case of our ViaScan service, our Heart Scan utilizes a CT scanner to determine the amount of calcium present, which informs you of your risk of developing heart disease long before any signs of the disease appear. Early indications of lung disease, such as early lung infections, which may cause chest pain, can be detected through a Lung Scan. To provide what Whites call total peace of mind, our Whole Body Scans scan your entire body’s overall well-being.
These preventive scans are especially worthwhile when you have experienced several documented incidents of chest aches. They can identify problematic cases before they escalate into emergencies.
Why would you utilize ViaScan to treat chest pain problems?
ViaScan understands you are afraid of chest pain, whether from dehydration or not. With our top-level imaging, you can look inside yourself and see exactly what’s happening inside. Whole Body Scan, the Heart Scan, and the Lung Scan give you and your physician the facts on making smart health decisions.
Heart or lung disease is what individuals do not realize that they have because the disease remains undetected until it is too late. The significance of preventive imaging then resides in the fact, i.e., it diagnoses an issue at an early stage, while it is easiest to tackle proactively. When you go through all the symptoms outlined above (like feeling chest pain, which presented itself because of dehydration), it is a lesson that you can still understand your body. Early detection can save your life.
Choose Our Preventive Heart Scan
Early Detection Saves Lives!
-
- Accurate
- Quick Result
- Affordable

Conclusion
Chest pains can be caused by dehydration, and it does not occur as rarely as people think. Should not misjudge chest pain. It involves knowing when it is time to hydrate, when it is time to relax, and when it’s time to run to the hospital. In any case, it’s best to be on the safe side. Continue drinking water throughout the day and remember to do so. However, remember that imaging procedures done to assess chest pain can provide concrete evidence of your heart and lung status. With high-tech scans using ViaScan, you receive the information and assurance needed to take care of your health. Book your preventive scan now and take the step that will give you peace of mind. You will be glad you did in the future.